Projects’ views
All figures are clickable to zoom on them.
Azureus
Description
Azureus (Vuze) is a BitTorrent client supporting multiple communication protocols such as I2P, Tor and WebTorrent.
- Link to the codebase: https://github.com/Corpus-2021/Azureus
View configuration
- Entry point classes:
com.aelitis.azureus.core.AzureusCoreComponent
- Usage orientation: OUT
- Usage level: 4
- Metrics source: SonarCloud
- Displayed metrics
- cognitive complexity (red-green) (range: 0 → 100)
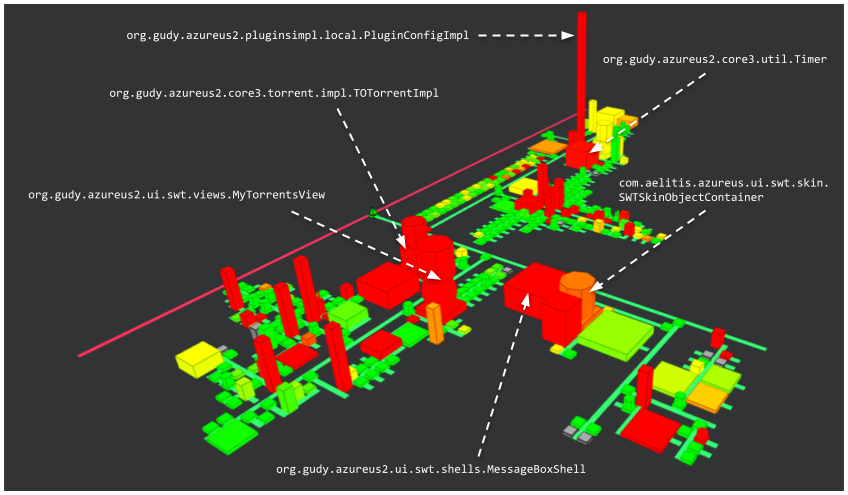
This view allows to visualize the main elements constituting the client:
MyTorrentsView represents the view of the torrent files downloaded by the user,
MessageBoxShell represents a message displayed to the user, configurable with different titles and messages,
Timer deals with the time management for download tasks,
TOTorrentImpl is the object representation of a torrent file.
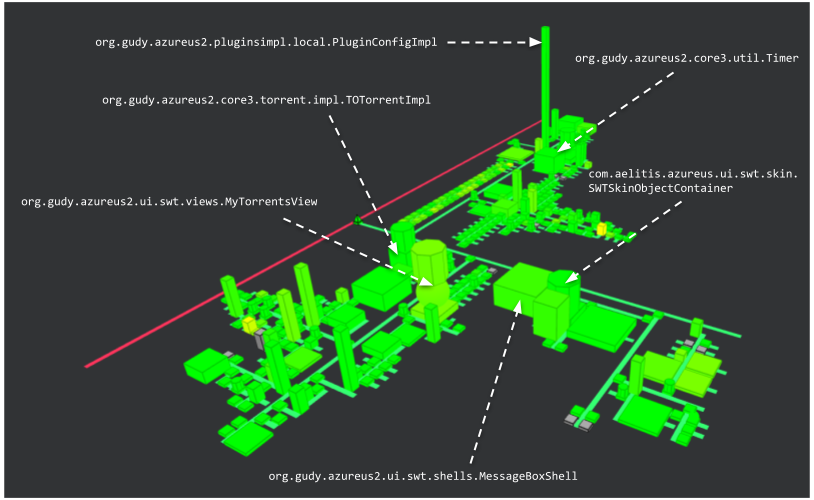
While we could compute the number of duplicated blocks, this metric is not relevant as even with low thresholds, no class particularly detach from the others, showing a global good quality with regards to this metric.
- Displayed metrics
- # duplicated blocks (red-green) (range: 0 → 25)
GeoTools
Description
GeoTools is an open source Java library that provides tools for geospatial data, such as map projections. An overview of the main features is available here.
- Link to the codebase: https://github.com/Corpus-2021/geotools
View configuration
- Entry point classes:
org.geotools.data.simple.SimpleFeatureSourceorg.geotools.map.MapContent
- Usage orientation: OUT
- Usage level: 4
- Metrics source: SonarCloud
- Displayed metrics
- cognitive complexity (red-green) (range: 0 → 150)
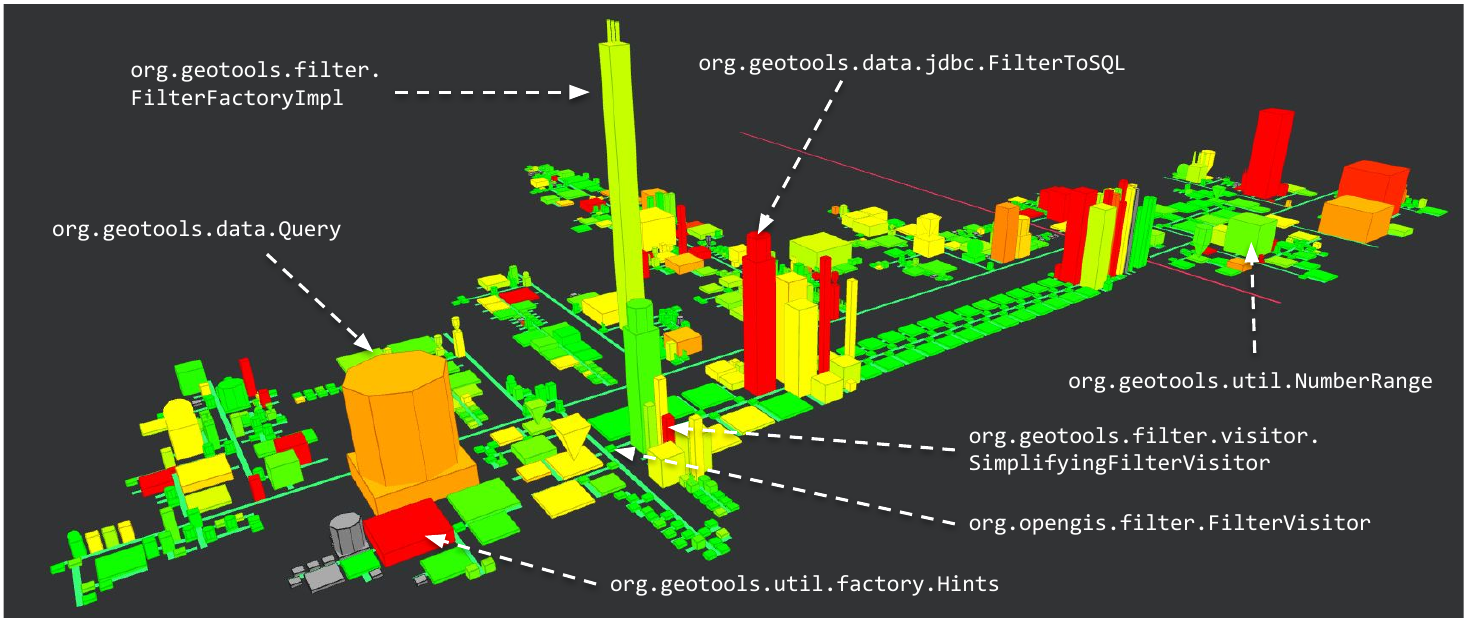
FilterFactoryImpl’s goal is to create filters allowing to select zones from a map.
These filters are used by Query to query information from a data source
and also by FilterVisitor that applies all the filters on the map.
The filters themselves are positioned on the long street initiated by FilterVisitor.
Finally, Hints allow to configure the renderers and grid processors, implemented using factories.
JDK
Description
The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a set of libraries allowing to build, compile and execute code using the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
- Link to the codebase: https://github.com/Corpus-2021/jdk
View configuration
- Entry point classes:
java.net.URIjava.net.URL
- Usage orientation: IN
- Usage level: 1
- Metrics source: SonarCloud
- Displayed metrics
- cognitive complexity (red-green) (range: 0 → 200)
- # duplicated blocks (cracks) (range: 0 → 20)
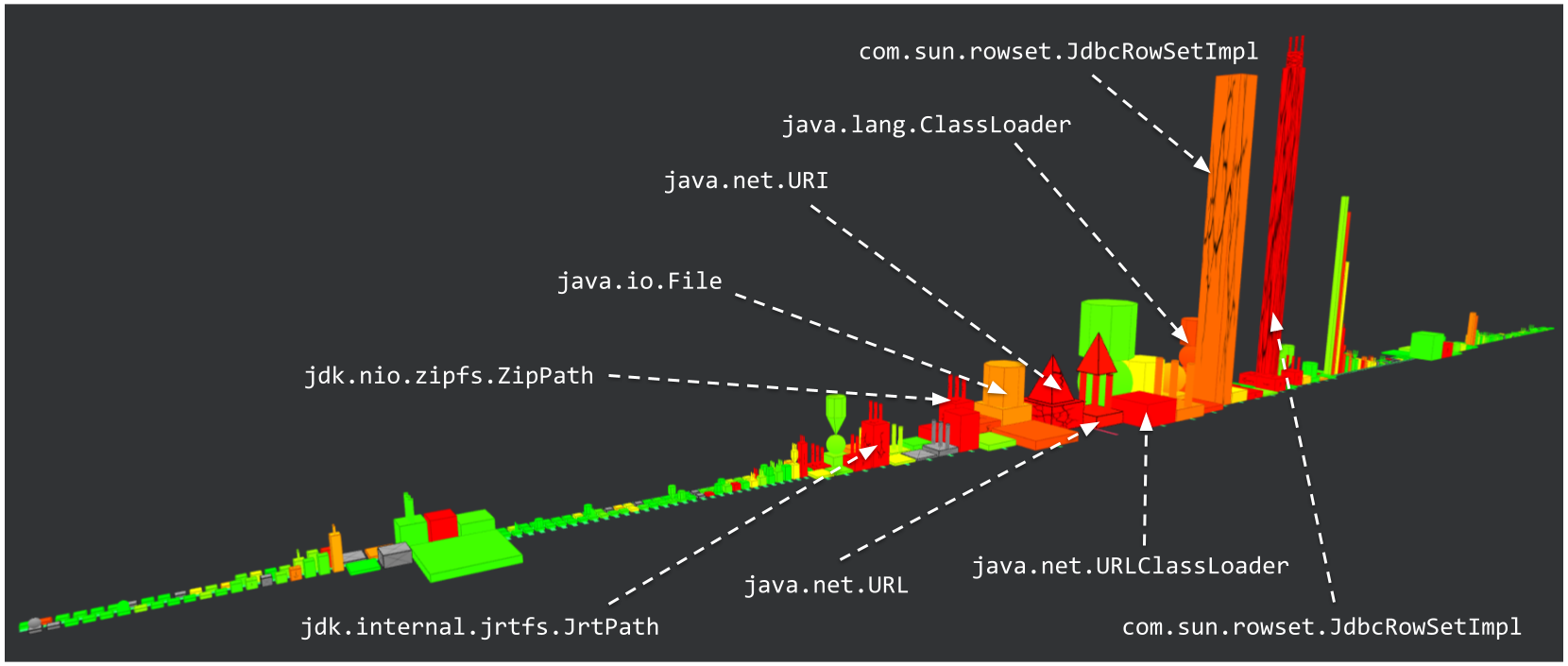
In this visualization, we can observe the types directly used by the URI and URL classes, such as File that represents a file on the system, and the ClassLoader.
Although this visualization does not explicit an important number of classes, it is already interesting to notice that the two classes having both an important cognitive complexity and an important number of duplicated blocks corresponds to two classes located in the com.sun package.
These classes are still present for legacy reasons to allow retrocompatibility with Oracle’s JDK. However, these classes are not part of the public API and Oracle itself recommends not to directly use them in Java programs as they can be refactored and/or moved at any moment.
(source: https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/faq-sun-packages.html)
JFreeChart
Description
JFreeChart is a Java charting library allowing to draw multiple types of charts.
- Link to the codebase: https://github.com/jfree/jfreechart/
View configuration
- Entry point classes:
org.jfree.chart.JFreeChartorg.jfree.chart.plot.Plot
- Usage orientation: OUT
- Usage level: 4
- Metrics source: Local SonarQube instance
- Displayed metrics
- code coverage (red-green) (range: 0% → 100%)
- # duplicated blocks (cracks) (range: 0 → 50)
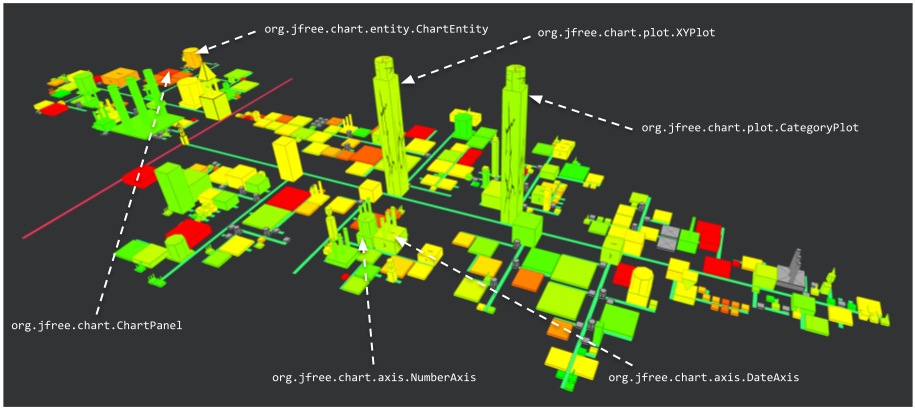
The variability in the types of charts can be seen with CategoryPlot and XYPlot correspond to bar charts and charts using two axes respectively.
Variability can also be observed at the axes level: NumberAxis and DateAxis are two types of axes, using either numerical values or dates.
Finally, ChartEntity represents an element constituting a chart (e.g. the plot itself, the title, the axes…) and ChartPanel represents the canvas where the plot is drawn.
Other views illustrating the evolution of JFreeChart’s metrics before and after the maintenance actions in the qualitative evaluation are available here.
JKube
Description
Eclipse JKube is a collection of plugins and libraries that are used for building container images using Docker, JIB or S2I build strategies. Eclipse JKube generates and deploys Kubernetes/OpenShift manifests at compile time too. It is the successor of Fabric8, and also provides a set of tools such as watch, debug, log, etc.
- Link to the codebase: https://github.com/eclipse/jkube
View configuration
- Entry point classes:
org.eclipse.jkube.generator.api.support.BaseGeneratororg.eclipse.jkube.generator.javaexec.JavaExecGeneratororg.eclipse.jkube.generator.api.Generator
- Usage orientation: IN/OUT
- Usage level: 7
- Metrics source: SonarCloud
- Displayed metrics
- coverage (red-green) (range: 0% → 100%)
- cognitive complexity (cracks) (range: 0 → 150)
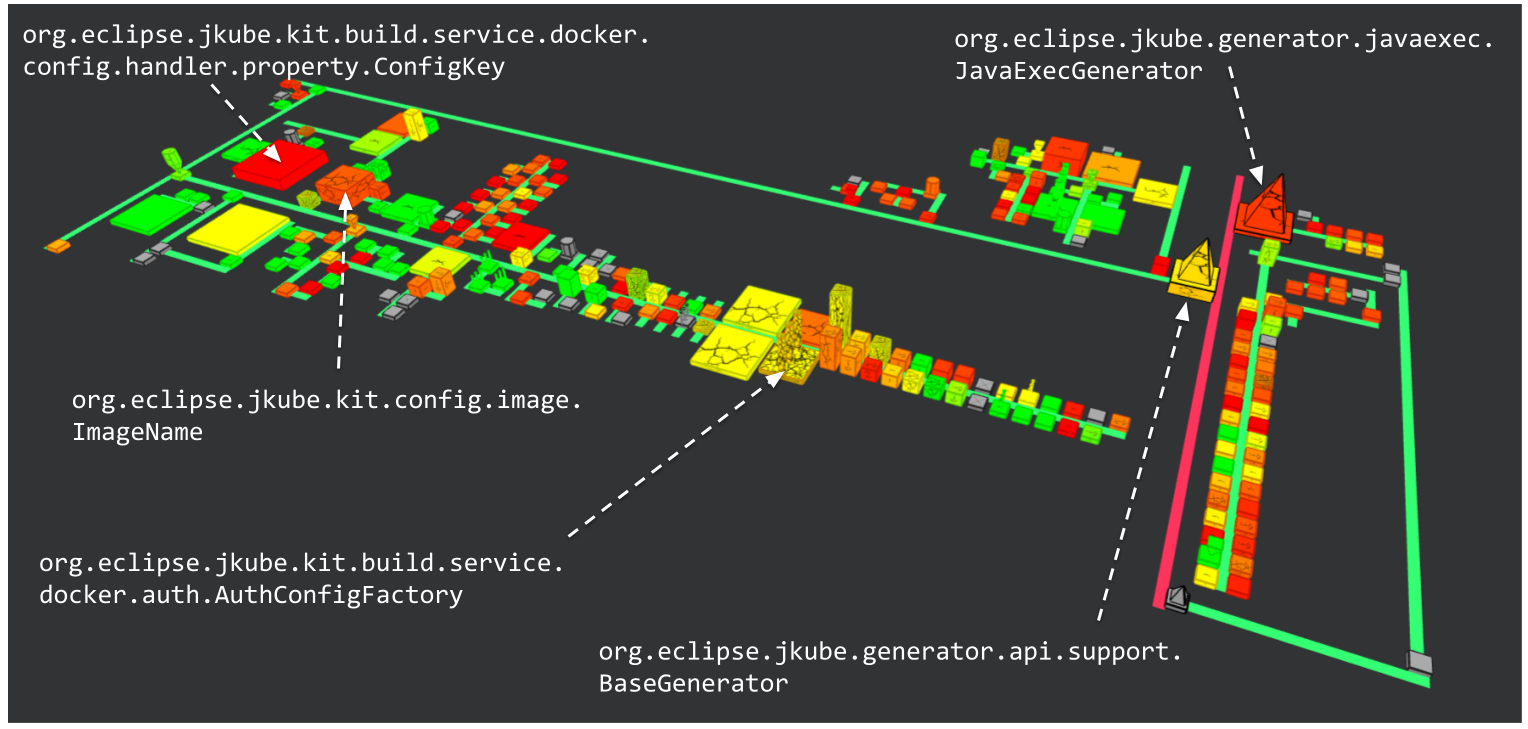
The Generators read the Maven build file to generate an image configuration.
ConfigKey enumerates the different configuration keys for the generated images.
ImageName is a helper class to help parse the name of a Docker image.
Finally, AuthConfigFactory generates an authentication configuration to communicate with the Docker registry.
OpenAPI Generator
Description
OpenAPI Generator allows generation of API client libraries (SDK generation), server stubs, documentation and configuration. This framework supports plethora of different implementation languages.
- Link to the codebase: https://github.com/OpenAPITools/openapi-generator
View configuration
- Entry point classes:
org.openapitools.codegen.languages.OpenAPIGenerator
- Usage orientation: IN/OUT
- Usage level: 6
- Metrics source: SonarCloud
- Displayed metrics
- coverage (red-green) (range: 0% → 100%)
- cognitive complexity (cracks) (range: 0 → 150)
DefaultCodegen corresponds to the default code generator.
CamelCaseLambda converts a given text sequence in CamelCase.
IJsonSchemaValidationProperties allows to validate the generated format of an expected JSON in queries of the generated API.
Spring framework
Description
The Spring framework provides a set of libraries to support component and service architectures in Java.
- Link to the codebase: https://github.com/Corpus-2021/spring-framework/
View configuration
- Entry point classes:
org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.BeanComponentDefinitionorg.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory
- Usage orientation: IN
- Metrics source: SonarCloud
- Usage level: 8
- Displayed metrics
- cognitive complexity (red-green) (range: 0 → 150)
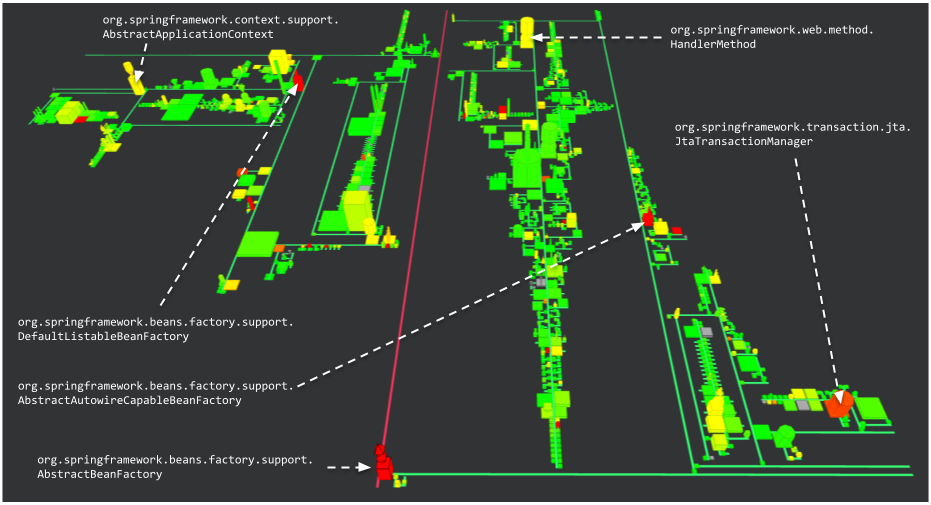
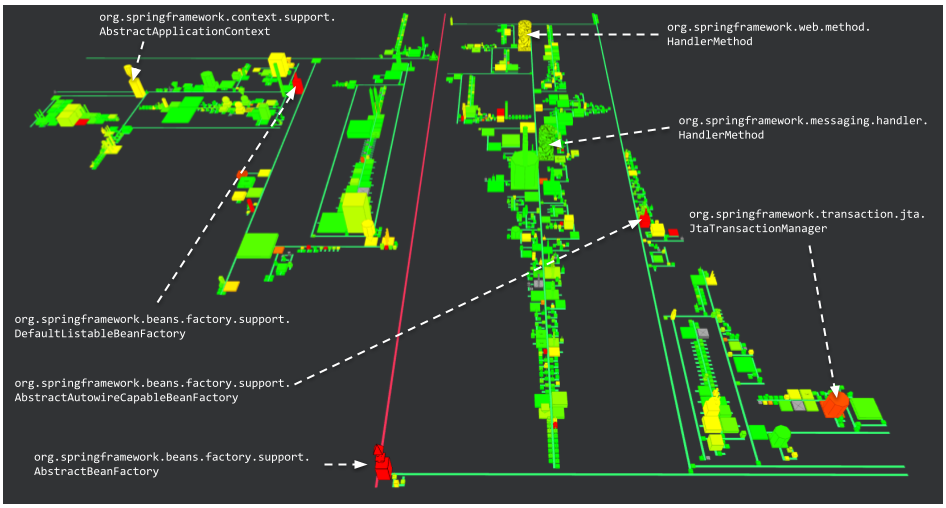
This view uses AbstractBeanFactory as an entry point, class that manages the creation of the beans, being objects used through dependency injection.
This view shows the classes using AbstractBeanFactory on 8 levels of composition.
The AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory class implements the default bean creation mechanism.
DefaultListableBeanFactory, on its side, allows to create beans and keep them in a list to allow quick lookup through names to find a bean for a given name.
MethodHandler provides easy access to properties of a bean’s method
JtaTransactionManager handles transations using the Java Transactions API (JTA).
AbstractApplicationContext provides an abstract implementation of the configuration for a Spring application.
While we could compute the number of duplicated blocks, this metric is not relevant as even with low thresholds, no class particularly detach from the others, showing a global good quality with regards to this metric.
- Displayed metrics
- cognitive complexity (red-green) (range: 0 → 150)
- # duplicated blocks (red-green) (range: 0 → 25)